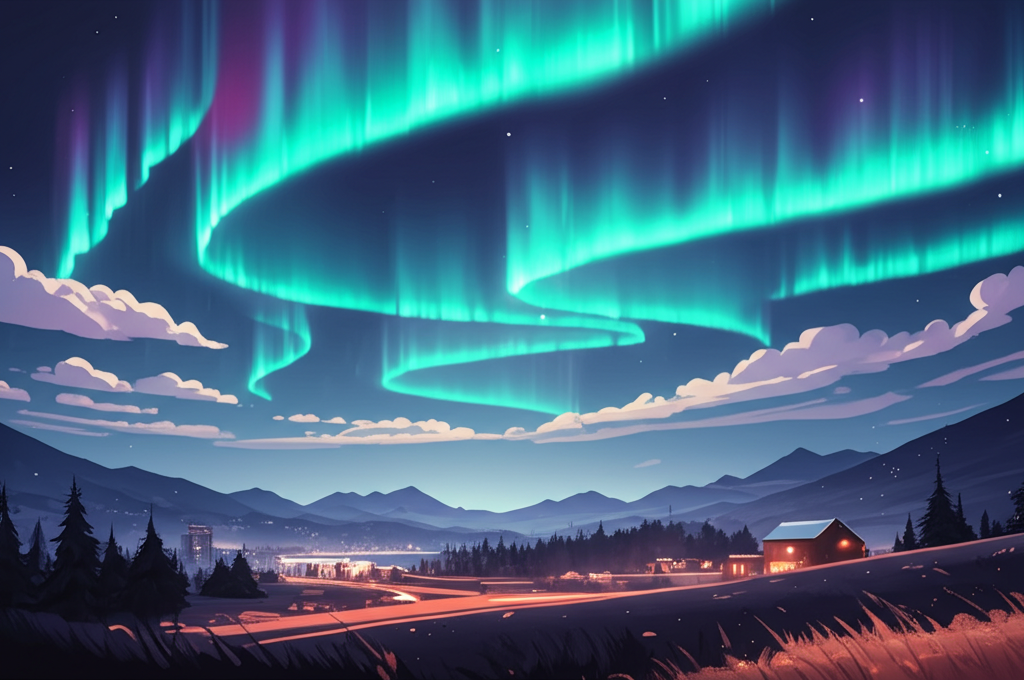
The phenomenon of the Aurora Borealis, commonly known as the Northern Lights, is a breathtaking natural spectacle that captivates observers with its ethereal dance of lights across the night sky. This celestial display is typically visible in high-latitude regions near the Arctic, but recent geomagnetic storm conditions have expanded its visibility to more southern latitudes, including several states in the United States. The Northern Lights occur when charged particles from the sun interact with Earth’s magnetic field and atmosphere, creating a mesmerizing array of colors that can range from green and pink to red and purple.
The Northern Lights are not a rare occurrence, but their visibility can be influenced by various factors, including solar activity and geomagnetic storms. These storms are disturbances in Earth’s magnetosphere caused by the solar wind, which is a stream of charged particles released from the sun. When these particles collide with Earth’s magnetic field, they can cause fluctuations that make the Northern Lights visible in regions that are typically outside their usual range. In recent forecasts, it has been predicted that these geomagnetic storms may bring the Aurora Borealis to more U.S. states along the Canadian border, offering a unique opportunity for residents and visitors to witness this stunning natural phenomenon.
Geomagnetic storms are classified based on their intensity, with stronger storms having a greater impact on Earth’s magnetic field and increasing the likelihood of auroral activity. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) monitors solar activity and issues forecasts for geomagnetic storms, providing valuable information for those interested in viewing the Northern Lights. According to NOAA, a minor geomagnetic storm is expected to occur, which may make the Northern Lights visible in about 15 states. These states include those along the northern border of the U.S., where the chances of viewing the aurora are highest. However, even in regions with a lower probability of visibility, such as northeastern Washington, northern Idaho, northern Montana, North Dakota, and northern Minnesota, there is still a possibility of seeing the lights under the right conditions.
The states with the highest chance of viewing the Northern Lights include Alaska, which is well-known for its frequent auroral displays, as well as parts of northern Canada. In the contiguous United States, the states along the Canadian border, such as Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, New York, Michigan, Wisconsin, and Minnesota, have a better chance of witnessing the aurora. However, the visibility of the Northern Lights can be affected by several factors, including cloud cover, light pollution, and the strength of the geomagnetic storm. To increase the chances of seeing the aurora, it is recommended to find a location away from city lights and with a clear view of the northern horizon. Additionally, checking the latest forecasts and auroral activity reports can help in planning a successful viewing experience.
The Northern Lights are not only a visual spectacle but also a subject of scientific interest. Researchers study the aurora to better understand the interactions between the sun and Earth’s magnetic field, as well as the dynamics of the upper atmosphere. The data collected from these studies can provide insights into space weather, which can have implications for satellite communications, navigation systems, and power grids. By monitoring the aurora and the conditions that lead to its formation, scientists can improve their ability to predict and mitigate the effects of geomagnetic storms on Earth’s technology and infrastructure.
In addition to their scientific significance, the Northern Lights hold cultural and historical importance for many communities. Indigenous peoples in the Arctic regions have long been aware of the aurora and have incorporated it into their folklore and traditions. For example, the Inuit people of Canada have various legends and stories about the Northern Lights, often associating them with spirits or ancestors. In modern times, the aurora has become a popular tourist attraction, drawing visitors from around the world to witness its beauty. This has led to the development of aurora-related tourism, which can provide economic benefits to local communities while also promoting awareness and appreciation for this natural phenomenon.
The Northern Lights are a reminder of the interconnectedness of the sun and Earth, as well as the dynamic nature of our planet’s magnetic field. The recent forecasts of geomagnetic storms bringing the aurora to more U.S. states offer a unique opportunity for people to experience this awe-inspiring display. Whether viewed from the comfort of one’s backyard or during a planned trip to a remote location, the Northern Lights are sure to leave a lasting impression. As we continue to learn more about the science behind the aurora and its cultural significance, our appreciation for this natural wonder only grows. So, if you find yourself in one of the 15 states with a chance of viewing the Northern Lights, take a moment to step outside and look up at the sky. You might just witness a spectacle that will stay with you for a lifetime.