Introduction: The Turbulent World of Ethereum
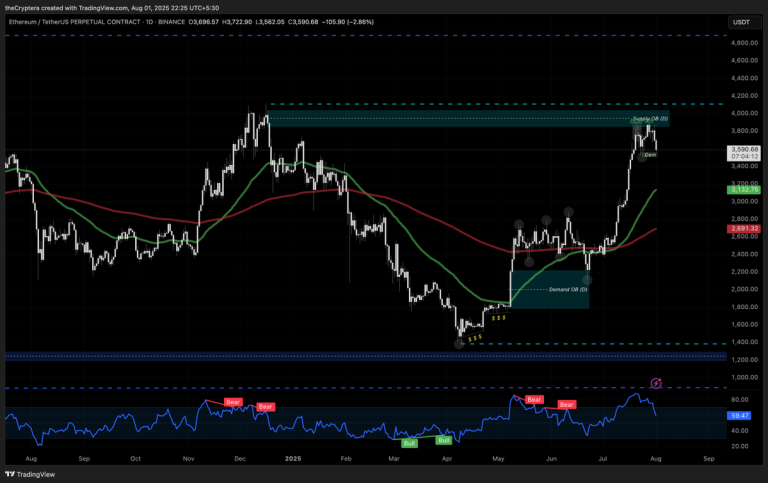
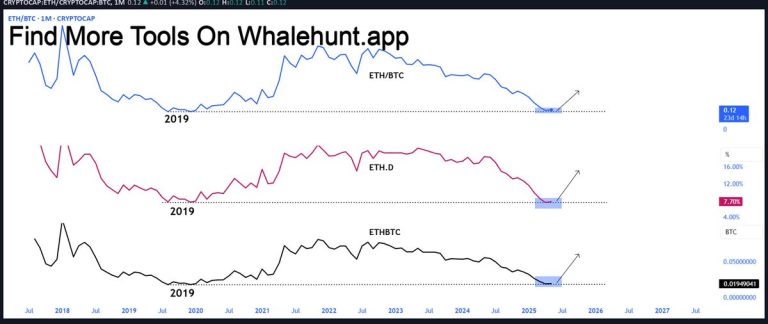
In the ever-volatile cryptocurrency market, Ethereum, the second-largest digital currency by market capitalization, has been experiencing significant price fluctuations. Recently, Ethereum’s price has plummeted to around $2,000, testing its 16-month low. This dramatic drop has left many investors and enthusiasts wondering: Why is Ethereum going down? To understand this trend, let’s dive into the key factors influencing Ethereum’s price.
Main Analysis
1. Macro-Economic Pressures and Trade Tensions
One of the primary reasons for Ethereum’s decline is the broader economic climate. Global trade tensions, particularly those stemming from U.S. policies, have created a risk-off sentiment among investors. Cryptocurrencies, often viewed as high-risk assets, tend to suffer when traditional markets turn bearish[1]. Recent announcements of tariffs on countries like Canada, Mexico, and China have further exacerbated this situation[1].
2. Massive Liquidations and Whale Activity
Another critical factor is the significant liquidation events in the crypto space. Large holders, or “whales,” have been offloading their ETH holdings, adding downward pressure on the price. On-chain data indicates that Ethereum’s supply on centralized exchanges hit a 12-month high, signaling heavy selling by major players[1]. Additionally, massive liquidations of long positions on leveraged markets have contributed to the price drop[1].
3. Technical Breakdowns and Bearish Indicators
Technical analysis also points to bearish patterns, suggesting a potential further drop if momentum doesn’t shift. Indicators like the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) and Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicate persistent bearish sentiment[1]. These technical factors have been compounded by recent market events, such as the Bybit hack and speculation over a potential Ethereum hard fork[3].
4. Competition and Network Challenges
Ethereum faces increasing competition from other blockchain platforms like Solana, which offers faster transaction speeds and lower fees[1]. The rise of Layer-2 solutions, while beneficial for scaling, has also shifted activity away from Ethereum’s base layer, reducing demand for ETH in some cases[1]. Furthermore, Ethereum’s shift to proof-of-stake has not fully achieved its intended deflationary effects, leading to an increase in supply and dampening investor confidence[1].
Conclusion: A Future in Flux
Looking Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
While Ethereum’s current situation seems bleak, there are potential catalysts for a rebound. Declining exchange reserves and institutional interest could signal reduced selling pressure and long-term confidence[1]. Proposed upgrades like EIP-7781 aim to address network performance and restore Ethereum’s deflationary status, potentially boosting sentiment[1]. However, overcoming macroeconomic headwinds and technical challenges will be crucial for Ethereum’s recovery.
In conclusion, Ethereum’s price drop is a complex issue influenced by a mix of economic, technical, and competitive factors. As the cryptocurrency market continues to evolve, Ethereum’s future will depend on its ability to adapt and innovate in the face of these challenges.
—
Sources:
– TradingView
– Westurner’s GitHub Pages
– Binance